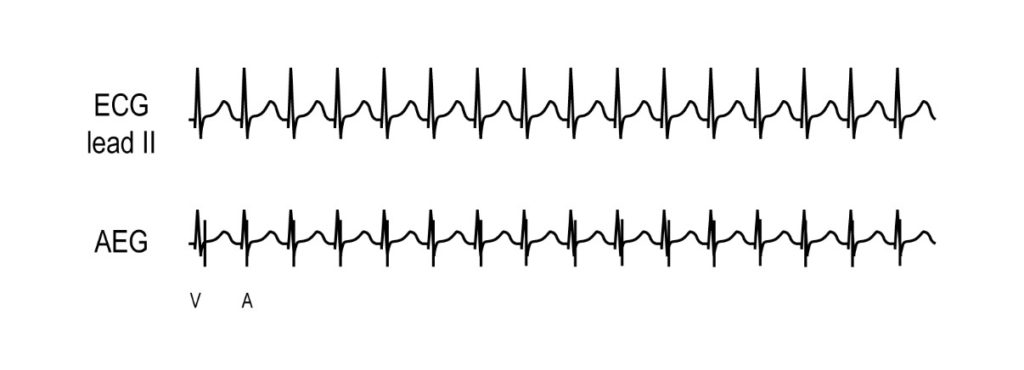
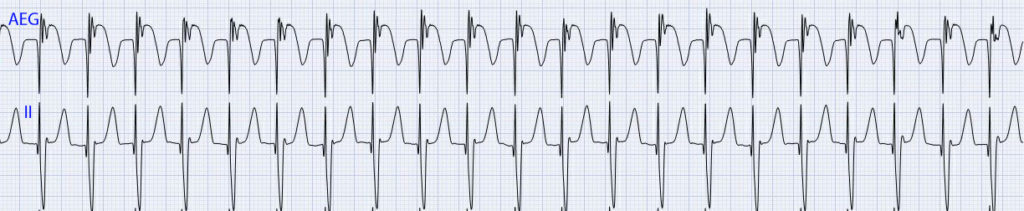
Background: JET is most commonly found in the post-operative setting. It is a tachycardia with a similar QRS appearance to the baseline QRS, and most often occurs within 48 to 72 hours of surgery. It typically demonstrates a gradual increase and gradual decrease of its rate in comparison to the abrupt increase seen with reentrant supraventricular arrhythmias. It can be especially difficult to diagnose on the surface electrogram, but readily identified with an AEG.
AEG: JET may show 1:1 AV conduction, or more ventricular than atrial signals. With 1:1 conduction, the AEG generally shows a ventricular signals with an atrial signal closely following or overlapping the terminal QRS complex. The AEG often appears very similar to AVNRT though JET generally shows rate variability and gradual onset. The above images both show JET with intact retrograde conduction.
Adenosine: JET is generally not responsive to adenosine.
Atrial Overdrive Pacing: Atrial pacing at a rate higher than the JET may suppress the arrhythmia. However, unless it has resolved or is controlled with other means, the rhythm typically returns when pacing is discontinued.