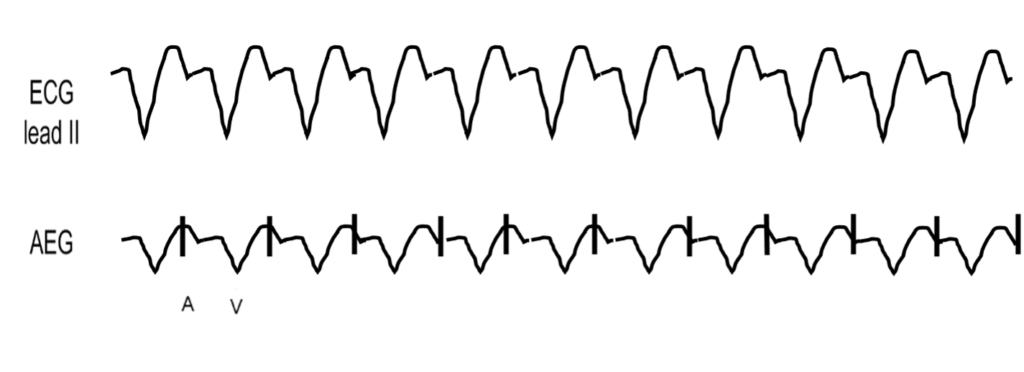
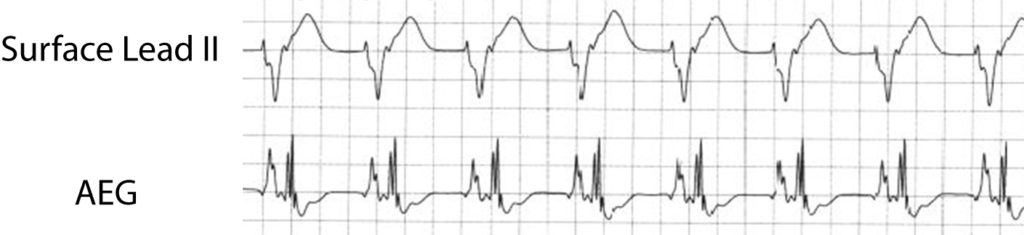
Background: An accelerated ventricular rhythm reveals a regular, wide complex rhythm with a relatively slow rate, usually within 15% of the sinus rate. This is typically better tolerated than the more rapid ventricular tachycardia.
AEG: The atrial to ventricular ratio is dependent on the retrograde AV nodal conduction and can show either a 1:1 atrial to ventricular ratio, or more ventricular than atrial signals. In comparison to an accelerated junctional rhythm, an accelerated ventricular rhythm has a morphology that is wide complex and distinct from the patient’s baseline QRS appearance. Here we show an accelerated ventricular rhythm with intact retrograde conduction.
Adenosine: An accelerated ventricular rhythm is generally not responsive to adenosine.
Atrial Overdrive Pacing: An accelerated ventricular rhythm can often be suppressed with (atrial or ventricular) pacing at a rate higher than the arrhythmia rate, but may return when pacing is stopped.